Instances¶
Instances are a great starting point for taking advantage of self service features and spinning up both VMs and containers. In Morpheus it may be advisable to cover the definition of a few terms used within the application so as to reduce confusion. These concepts are also covered in greater detail in the Provisioning Concepts section.
- Instance
A set of containers or virtual machines that can correlate to a single horizontally-scalable entity or a service suite, like a database. It is important to note that an Instance can contain one or more containers/VMs depending on the Instance type and configuration.
- Container
Typically a docker container provisioned via a Morpheus Docker host.
- Virtual Machine
A virtualized compute server provisioned onto various hypervisor hosts.
The top of the main Instances page shows overall statistics for the listed Instances, including count, status, and resource utilization. You can search for Instances by name, or filter by group, instance type, or category.
Note
Instances listed are determined by group access and role permissions. When filtered to show Instances of “All Statuses”, any Instances which are in a state of pending removal due to a delayed delete policy in place are not shown under this filter. Instead you must filter for “Pending Removal” to see these Instances and prevent deletion, if desired.
The Instance list contains important information about each instance, including the instance name, environment tag, instance type icon, IP address and port info, Instance version, the number of virtual machines or containers in the instance, the group the instance is in, and the cloud or clouds the instance is in.
Creating Instances¶
The Instance catalog is the one-stop shop for selecting items to be provisioned and pieced together. It contains not only basic container and VM options but also tailored services for SQL databases, NoSQL databases, cache stores, message busses, web servers, and even full-fledged apps. The list contains a lot of items to choose from and they are represented to the user based on what provisioning engines are enabled and integrated in the Morpheus environment.
To get started, simply click the + Add button in the upper right of the Provisioning > Instances section. A modal will display allowing the catalog to be searched. Once an item is selected it is just a matter of following the steps through the wizard.
Tip
The Instance catalog can be customized via role-based access control (RBAC) thereby restricting access to non-sanctioned catalog items, as well as added to via the Library section. It is completely customizable.
The next step will ask for a Group and Cloud to be selected. The Group is an abstract representation that can contain multiple cloud integrations. Clouds can be in multiple Groups and Groups are also useful for using RBAC to restrict provisioning access and set retainment policies. If the environment is new and these do not yet exist, it may be advisable to refer to one of our starter guides, such as the guide on getting started with Morpheus and VMware. The wizard continues by allowing us to choose a name for the Instance as well as an environment.
Note
Currently the Environment option is mostly useful for presenting the user with informative metadata around the Instance when coming back to it later.
Moving on, it is now time to configure the Instance. Depending on the Instance Configuration that is chosen, fields will change. This can include cloud-specific fields (i.e. Datastore for VMware or Network). There will also be options like setting an initial user account. Some of these fields are optional and will be represented as such.
Configuration options provided in this screen are very powerful. An example is MySQL where a Master/Slave or Master/Master layout can be selected. These configurations will automatically deploy two MySQL VMs or containers and link them together to provide replication. These types of configurations exist for a wide range of Instance types and are optimized for high performance and scale. It is even possible to provision entire sharded MongoDB clusters.
One last step before the Instance can be provisioned is the Automation step. This wizard step may or may not appear depending on the capabilities of the Instance type or previous configurations in the account. It is here one can easily select a post-provisioning workflow to run (see more on Tasks and Workflows elsewhere in Morpheus documentation), assign a load balancer, or even configure the backup job that gets created.
Now that the steps are completed for provisioning the selected Instance type, simply review your selections and complete. The Instance will automatically show up in the Instances list and its provisioning state will be represented. Depending on what was provisioned this step can range from seconds to minutes (typically a container configuration will be rather quick if the Instance type has previously been provisioned before).
Converting Discovered Resources to Managed Instances¶
When creating new cloud integrations (or updating existing ones), users may opt for Morpheus to onboard any existing resources that currently reside in the Cloud. For example, these may be virtual machines that exist on vCenter hosts prior to integration with Morpheus, EC2 instances pre-existing on an Amazon AWS account, or virtual machines that are running on a KVM host. With the Add/Edit Cloud modal open, mark INVENTORY EXISTING INSTANCES for Morpheus to automatically onboard these resources. Not only will Morpheus inventory these instances at the time the cloud is integrated (or updated), it will also continue to poll the target cloud every five minutes (by default) for newly added or removed servers. Users can see these discovered servers by looking in Infrastructure > Compute. Depending on the type of resource, it may appear on the Virtual Machines tab, the Containers tab, or another tab. Additionally, we can see a list of discovered servers on Cloud detail pages (Infrastructure > Clouds > Selected Cloud). Just click on the tabs for VMs, Containers or Hosts tab. Discovered resources will be indicated as such whereas containers which are associated with a managed Instance will be marked as a “Managed”.
Additionally, Morpheus allows users to convert discovered resources into managed Instances. Begin from the server detail page (Infrastructure > Compute > Virtual Machines > selected machine) and from the ACTIONS menu select “Convert to Managed”. At this point, we must make a number of selections:
Assign to the primary Tenant or one of the Subtenants
Select a Group (this dropdown contains a filtered list of Groups which the associated Cloud is in)
Username and password for a seeded account
Opt to install Morpheus Agent or not (for more on Morpheus Agent, click here)
Select the Instance Type which should be associated with the new Instance containing this VM
Select a version number for the Instance (such as 20.04 for a basic Ubuntu Instance)
Select a Layout, Instance Types often have multiple Layout configurations
Identify the operating system
Select a Plan (this dropdown contains a filtered list of plans which correlate to the size of the VM)
Finally, click EXECUTE. Once this process is completed, the server will be indicated as “Managed” in the servers list. Additionally, a new Instance will appear on the Instances List page (Provisioning > Instances). We can now work with it in the same way we can work with any other Instance, such as by adding it to an App or expanding the Instance horizontally with added nodes.
Instance Details¶
The instance detail page is where you can view and fully manage an instance. To get to an instance detail page, navigate to Provisioning > Instances, and click on an Instance. Please note Instance details and actions will differ between Instance types and user permissions.
There are several sections within an Instance page that provide useful capabilities to the user.
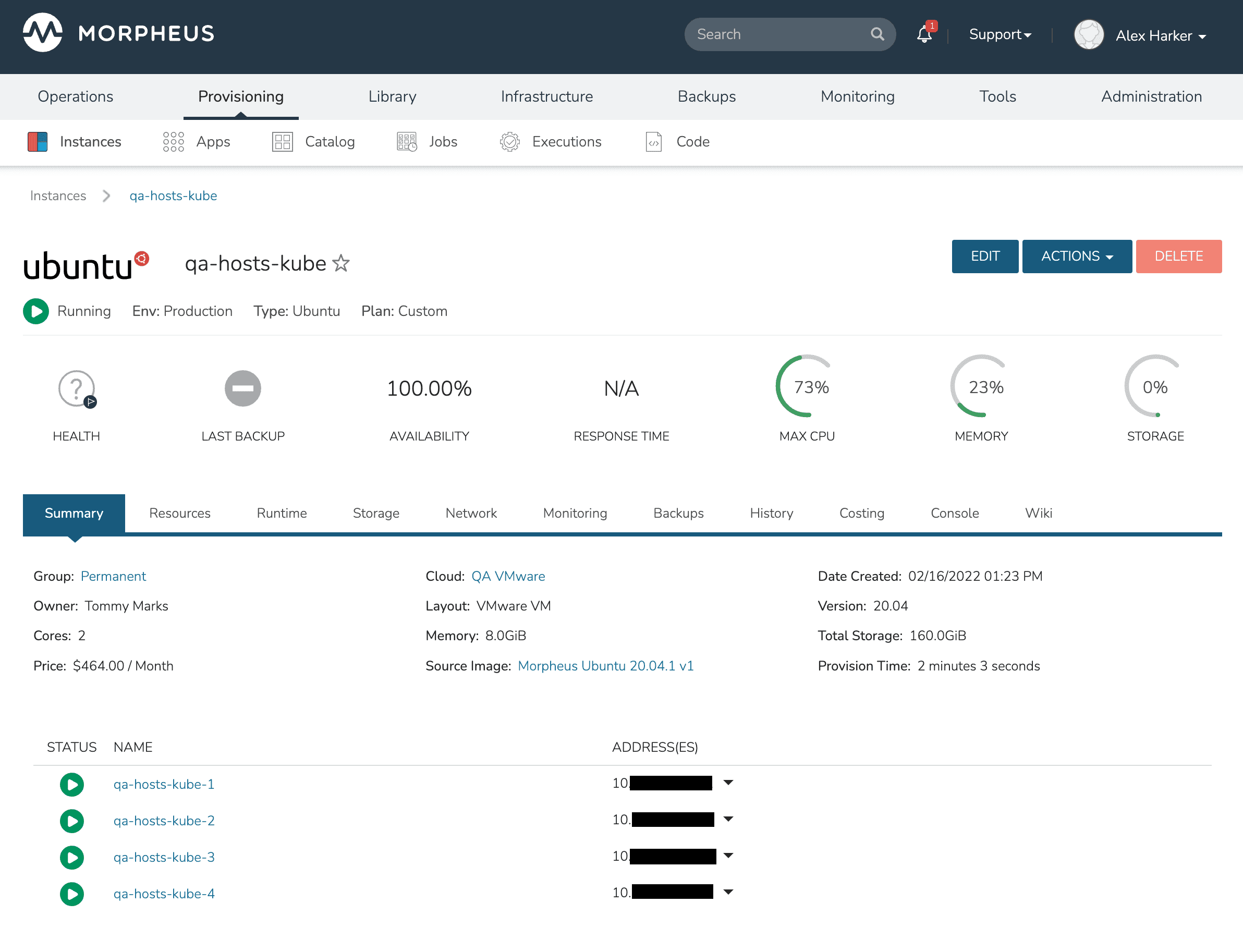
- Summary
Basic information, stats and status information
- Deploy
Track deployment history for instance types that support deployments or manually kick off a deployment (only visible for Instance Types that support deployments)
- Settings
Some Instance Types support custom configuration settings (for example, MySQL presents the my.ini)
- Resources
VMs, containers, or other resources associated with the Instance are listed here. Some Instance Types, such as XaaS Instances, will not have resources and the tab is not displayed
- Runtime
View the environment variables presented to the Instances or exported to the Instances via Apps (more on this in the Apps section). Users may also see Imported environment variables that may be referenced by the running Instance.
For Instances that support load balancing and auto scaling, configure auto scaling thresholds and load balancer settings in the Scale subsection that pertain to a particular Instance.
The software subsection will show any tracked software which is Installed as part of the provisioning process and is being tracked.
- Storage
See storage information associated with the Instance including the list of volumes and controllers which are associated with each machine that makes up the Instance.
- Network
Useful for configuring network interfaces for your VMs or security groups which allow access to the Instance.
- Monitoring
Quick summary of the monitoring system and all checks that were configured to test the state of the Instance. Stats views (memory, cpu, etc.) can be zoomed out to a 90-day view if desired (in global settings, ensure your stats retention setting will support this). Logs and guidance for the individual Instance are also shown in their respective subtabs.
- Backups
Quick backup dashboard. Useful for viewing historical backups and snapshots as well as adding new backup jobs.
- History
See historical information related to automation which has been run against the Instance. This is useful for examining automation which was run as part of a phase of a Provisioning Workflow. Users can also drill into the Workflows to examine individual Tasks, including viewing the output from these Tasks to confirm success or troubleshoot issues.
- Costing
Invoices pertaining to the Instance are displayed here. See the Instance level or host level invoices along with individual line items. In the History subtab view historical pricing data to monitor trends. In the Prices subtab view any prices which have been created and used to build a metered costing profile for the workload.
- Console
Access the Instance or container via a client-less Console supporting SSH, RDP, VNC, or even hypervisor-level remote consoles.
- Wiki
View the Wiki page for this Instance or edit the existing Wiki page (which may currently be blank). The content field supports markdown formatting, see the main Wiki section of Morpheus documentation for additional details.
Managing Instances¶
Instance actions allow you to perform numerous management tasks on instances. The actions available depend on the instance type, hypervisor, roles permissions, and instance state.
- Edit
Edit the Name, Description, Environment, Group, Metadata, Tags, and Owner for the Instance.
- Delete
Deletes the Instance.
Important
Deleting an Instance will delete the actual VM’s or Containers and cannot be undone, unless a Delayed Removal policy has been applied prior to the Deletion. To delete Instances without deleting associated VM’s, delete the Instances VM record(s) from the Infrastructure section with “Remove Infrastructure” deselected and select “Remove Associated Instances” in the VM delete modal options. This will delete the records in Morpheus but leave the infrastructure in place.
Tip
You can change the owner of an instance easily by selecting the edit button and entering a new owner in the corresponding field.
Actions¶
Available options in the Actions dropdown can include:
- Suspend
Puts the VM in a suspended state without shutting down the OS.
- Stop/Start/Restart Service
Stops, Starts or Restarts the service associated with the Instance Type.
- Stop/Start/Restart Server
Stops, Starts or Restarts the Virtual Machine.
- Import as Image
Clones and exports VM in its current state to target Storage provider and adds Virtual Image Record with metadata matching the source Instance’s configuration.
- Clone to Image
Clones and converts VM in its current state to image in the source Cloud and adds Virtual Image Record with metadata matching the source Instance’s configuration.
- Lock/Unlock Instance
A locked instance cannot be deleted until it is unlocked.
- Reconfigure
The Reconfigure action allows service plan, disk, cpu, ram, networks and storage controller changes. Available options depend on the instance type and service plan configuration. Some resize actions require an instance restart.
- Clone
Creates a new Instance from the Instance at its current state.
- Backup
Immediately executes a backup of the Instance. Only available for Instances with backups enabled.
- Run Workflow
Presents workflow options and then immediately runs selected Workflow on the Instance. Workflows can be created in the Library > Automation section.
- Run Script
Presents Script options and immediately executes selected Script on the Instance. Scripts can be created in the Library section.
- Apply Template
Presents Template options and immediately applies selected Template to the Instance. Templates can be created in the Library section.
- Add Node
Adds an additional node to the configuration. Additional options and configurations are required in the add node wizard depending on instance configuration and type.
- Eject Disk
Ejects attached disk/iso.
- Add Slave
Adds a database slave in the Instance.
- Change Master
Changes the database Master node in an Instance.
- Clone to Template (VMware)
Creates a new VMware Template from the Instance with corresponding Morpheus Virtual Image record.
Tip
Scrolling down in the Actions dropdown may be necessary to see all options.
Performing Instance Actions¶
Select the Provisioning link in the navigation bar.
Click the Instance from the list of instances you wish to perform an action on.
Click the Actions drop down button and select an Action.
Notes¶
Every Instance has a Wiki section for adding useful information about the Instance. Wiki can be added by selecting the Wiki tab button on the bottom of Instance Detail pages. Instances with associated VMware VM’s will bi-directionally sync Morpheus Instance Wiki content and VMware VM Notes. See the Wiki Section for more details.
Tip
Markdown Syntax is supported in Wikis.