Identity Sources¶
Administration > Tenants > (Selected Tenant) > Identity Sources Administration > Users > Identity Sources
Overview¶
Morpheus can integrate with many of the most common identity source technologies, such as Active Directory, Okta, and many others. These can be configured via the Identity Sources button on any Tenant detail page (Administration > Tenants > Selected Tenant) or on the Users list page (Administration > Users). These integrations map roles within these sign-on tools to equivalent roles in Morpheus so at first log in users are assigned the appropriate role.
Active Directory¶
Overview¶
Active Directory is Microsoft’s primary authentication service. It is widely used in enterprise organizations and even in Microsoft cloud services. While Active Directory also supports LDAP protocol support (which Morpheus can integrate with as well), Morpheus includes a dedicated identity integration type specifically for Active Directory. By integrating Active Directory, Morpheus administrators can fully offload the work of managing the user lifecycle to Active Directory. Creating new users, applying roles to users, updating basic user data, disabling users, and more can be handled in Active Directory and automatically filtered down to Morpheus. This section includes an example integration walkthrough as well as additional details on the integration feature set.
Note
Caution should be used when integrating more than one Active Directory identity source with the same Morpheus Tenant. You must ensure the users on each identity source are unique users or that the two domains use different naming conventions for users.
How It Works¶
In Morpheus, identity sources (if used) are configured per Tenant. In order to see an identity integration or create a new one, navigate to a Tenant detail page (Administration > Tenants > Selected Tenant) and click IDENTITY SOURCES. From this page we can add a new identity source or click the pencil (✎) icon next to an existing identity source to view or edit it. Any configured identity source will apply to just one Tenant and they cannot be shared. One scenario where this is especially useful is in an MSP appliance where each Tenant is a siloed environment for a specific customer. The customer’s own existing Active Directory server and groups can be leveraged to build Morpheus user accounts with correct role mapping automatically.
When configuring an Active Directory integration in Morpheus, AD groups are mapped to Morpheus roles. When the user logs in for the first time, Morpheus adds the new user account with correct name, email address, and applies one or more roles depending on configuration. Going forward, Morpheus will sync down any changes to the user, including any role changes based on changes to the user’s associated AD groups or updated passwords. Additionally, disabling a user in AD will prevent them from accessing Morpheus.
Important
Morpheus will connect over port 389 for non-secure LDAP and port 636 for secure LDAP. Ensure that Morpheus is able to talk to the AD server on the proper port.
Example Integration¶
In a simple example, we have an Active Directory server which has two groups relevant to Morpheus, “Morpheus Users” and “Morpheus Admins.” We will configure Morpheus so that only users in the “Morpheus Users” group can access Morpheus in any capacity. Users who are also in the “Morpheus Admins” group will take on the System Admin role in Morpheus. We’ll see later when the integration is configured how Morpheus roles can be mapped to AD groups. In the same AD server, I have two users. John Smith is in groups “Morpheus Users” and “Morpheus Admins”. John Jones is only in the “Morpheus Users” group.
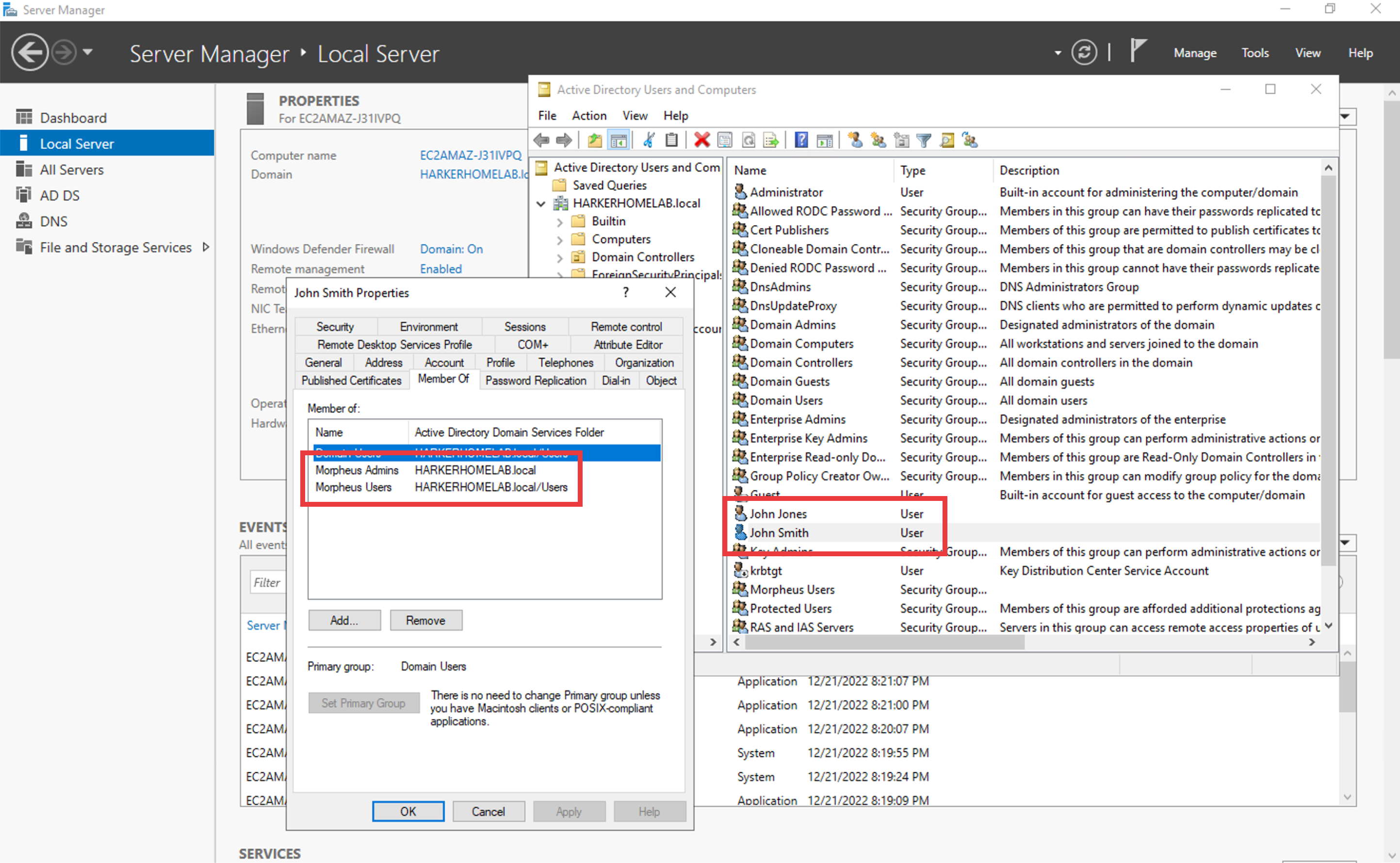
Knowing the AD scheme and the requirements for Morpheus user roles, we can begin the process of creating the integration. Identity integrations are specific to each Tenant so begin by navigating to the Tenant detail page (Administration > Tenants > Selected Tenant) and clicking IDENTITY SOURCES. On setting the type to “Active Directory,” the form will update with the needed fields. Note the following basic fields:
AD SERVER: The IP address or hostname for the Active Directory Server
DOMAIN: The AD domain in which the relevant users and groups reside
BINDING USERNAME: A server user which has access to relevant objects on the AD server. In my example, I’ve used the in-built Administrator user which is the easiest option. Other users may be used depending on your organization’s IT security policies but the integration with Morpheus will not work properly if the user does not have the needed access
BINDING PASSWORD: The password for the user in the prior field
With the basic configurations completed, the remaining configurations will affect Morpheus user and role generation. A REQUIRED GROUP is optional and is a group the user must be in to have any Morpheus access. Here we require that users be in the “Morpheus Users” group. A DEFAULT ROLE is required and will be assigned to all users regardless of any additional roles they may be assigned based on their AD group membership. Beyond that, all other Morpheus roles will be listed here and an AD group name can be associated with as many as you required. In this example, we are giving users in the “Morpheus Admins” group the Morpheus System Admin role. Though we did not use them, it’s worth pointing out that ENABLE ROLE MAPPING PERMISSION will give administrators in the Tenant the ability to update the AD role mappings (though they will not have access to the core integration fields such as AD SERVER, DOMAIN, or binding user details). MANUAL ROLE ASSIGNMENT allows users to manually update Morpheus roles outside of the automatic mappings created by the AD integration.
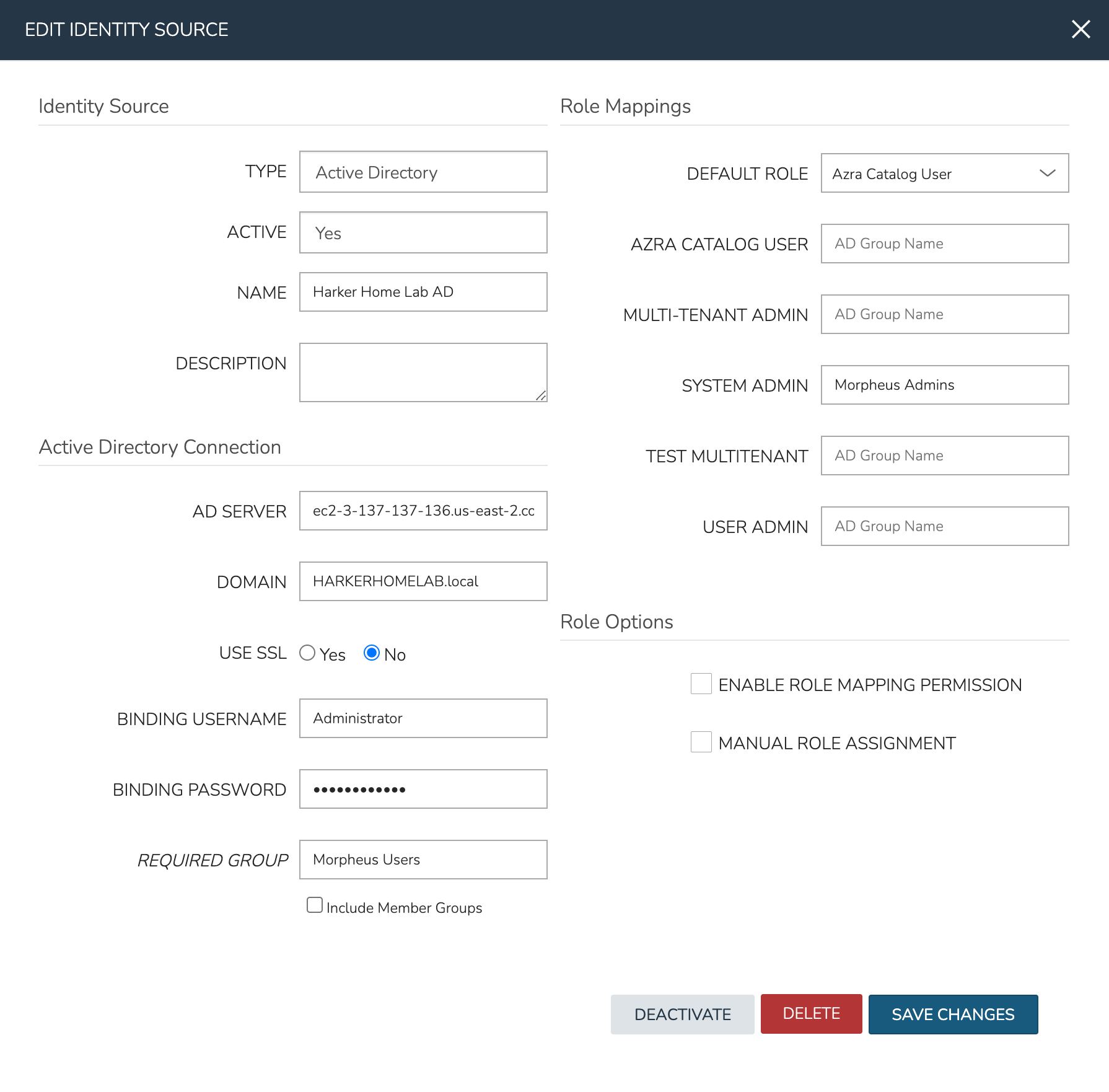
With the above integration steps completed, users can now log into Morpheus and a user account with correct roles will automatically be created. In our example case, John Smith has logged in and we can see he is assigned the default role as well as the System Admin role based on his AD group associations. Going forward, Morpheus will continue to sync any changes to these users. For example, Morpheus roles may be updated based on changing AD groups or user access may be completely revoked by disabling the user in AD.
Adding an Active Directory Integration¶
Navigate to Administration > Tenants
Select a Tenant
Select IDENTITY SOURCES
Select + ADD IDENTITY SOURCE
Set the TYPE to “Active Directory”
Populate the following:
- Name
A friendly name in Morpheus for the AD integration
- AD Server
The Hostname or IP address of AD Server
- Domain
The AD domain in which the relevant user and group objects reside
- USE SSL
Indicates whether SSL should be used for communication with the AD server. Morpheus will connect over port 389 for non-secure LDAP and port 636 for secure LDAP, ensure Morpheus can connect to the AD server over the correct port
- Binding Username
A username for a service account which has access to relevant objects (users, groups, etc.). For ease, the “Administrator” user may be used
- Binding Password
The password for the above account
- Required Group
The AD group users must be in to have access (optional, see example in the prior section)
- Default Role
The default role a user is assigned when they are in the required group or if no specific group mapping applies to the user (see example in prior section)
- ENABLE ROLE MAPPING PERMISSION
When selected, Tenant users with appropriate rights to view and edit Roles will have the ability to set role mapping for the Identity Source integration. This allows the Tenant user to edit only the role mappings without viewing or potentially editing the basic Identity Source configuration (AD server, domain, binding user details, etc)
- MANUAL ROLE ASSIGNMENT
When selected, administrators can manually edit Roles for users created through this identity source integration from the user detail page (Administration > Users > Selected user)
Note
For more on Identity Source role mapping permissions, see the associated guide in our KnowledgeBase.
Select SAVE CHANGES.
Now allowed AD users can login to Morpheus via their Active Directory credentials and a User will be automatically generated to Morpheus with matching metadata and mapped Role permissions.
Note
Sub-tenant Morpheus API authentication for Active Directory generated users is not currently supported.
Troubleshooting¶
If you’re unable to get the Active Directory integration to work, the following troubleshooting steps may be useful to ensure your appliance can talk to the Active Directory server.
Open firewall ports
Source: Morpheus appliance
Destination: AD server’s FQDN or IP address
Non-SSL AD integration: TCP-389
SSL AD integration: TCP-636
Checking open LDAP connections from the Morpheus appliance
Connect to a Morpheus appliance box and run the following:
$ sudo lsof i- | grep :ldap
Check LDAP connectivity from the Morpheus appliance
Connect to a Morpheus appliance box and run the following. Be sure to replace the placeholder values in the command with the correct values for your environment:
$ ldapsearch -x -h xx.xx.xx.xx -D "binding-user@acme.com" -W -b "cn=users,dc=acme,dc=com"
Run tcpflow from the Morpheus appliance for non-SSL enabled AD identity Integrations
Use tcpflow from the Morpheus appliance and then start the identity source configuration once again. Keep in mind this will only work for AD servers which are not SSL enabled:
$ sudo tcpflow -i any -c -v port 389
Check the AD and domain controllers event logs
Check the event logs for LDAP queries from the Morpheus appliance to ensure network connectivity.
Azure Active Directory SSO (SAML)¶
Azure Active Directory Single Sign-on can be added as a Identity Source in Morpheus using the SAML Identity Source Type. The Azure AD SSO configuration is slightly different than other SAML providers, and this guide will assist in adding a Azure AD SSO Identity Source.
Create Azure Enterprise Application¶
Login to the Azure Portal
Navigate to:
Azure Active Directory > Enterprise ApplicationsClick the
+ New applicationbutton at the topClick the
+ Create your own applicationbutton at the topEnsure
Integrate any other application you don't find in the gallery (Non-gallery)is selected and enter a name for the app. Common examples are:MorpheusSSOClick the
Createbutton at the bottom and wait for it to completeOnce created, you’ll be in the
Overviewof the application created. Navigate to theSingle sign-onsection from the left paneChoose
SAMLas the Single sign-on methodCopy both the
Login URLandLogout URLin Step 4, we’ll need these in some of the next stepsBefore we can continue configuring the application, the configuration needs to be generated in Morpheus for more data
Create an Azure AD SAML Integration in Morpheus¶
Azure requires inputting the Identifier (Entity ID) and Reply URL (Assertion Consumer Service URL) in the Azure SSO configuration before it provides the Endpoints and Certificate
necessary to add the Integration into Morpheus. In order to get the Identifier (Entity ID) and Reply URL (Assertion Consumer Service URL) to input into Azure SSO configuration,
we need to create a Azure AD SAML SSO integration in Morpheus first.
To add the integration:
Login to Morpheus
Navigate to Administration > Tenants
Click a tenant hyperlink
Click the IDENTITY SOURCES button in the Tenant detail page
Click the + ADD IDENTITY SOURCE button
Select
Azure AD SAML SSOfrom theTYPEdropdownAdd
Name
(Optional) Description
Paste the
Login URLcopied from Azure into theLOGIN REDIRECT URLfieldPaste the
Logout URLcopied from Azure into theSAML LOGOUT REDIRECT URLfield
This is the minimum information needed for now, which will let us generate the details needed from Morpheus. We’ll return to this configuration page later to enter more information.
Click the SAVE CHANGES button
Important
Setting SAML REQUEST to “No Signature” and SAML RESPONSE to “Do Not Validate Assertion Signature” is allowed but not recommended for security reasons.
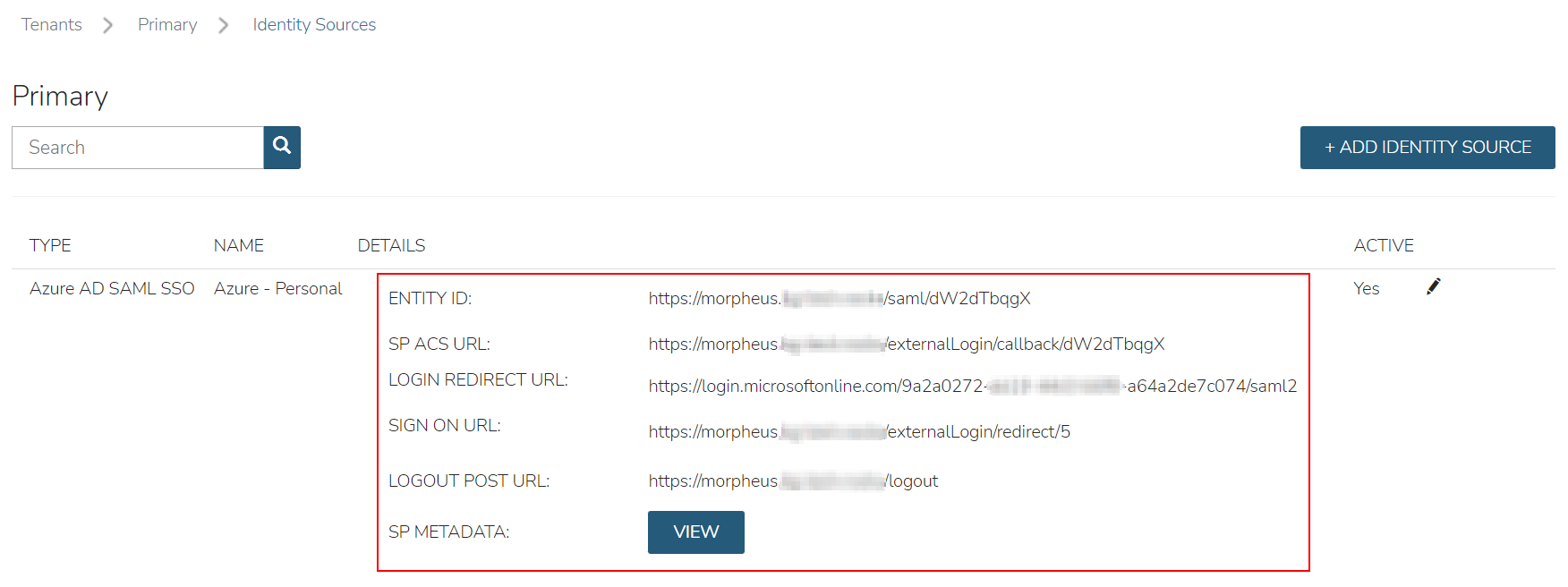
Upon saving, the Entity ID (Identifier (Entity ID)) and SP ACS URL (Reply URL (Assertion Consumer Service URL)) will be provide in the Identity Source list view. Copy these for use in Azure SSO configuration.
Configure Azure Enterprise Application¶
This guide assumes an Azure AD Enterprise Application has already been created. Please refer to documentation above, if this has not already been configured.
Navigate to:
Azure Active Directory > Enterprise Applications > Single sign-onChoose
SAMLas the Single sign-on methodOn Step 1 (
Basic SAML Configuration), click theEditbutton and enter the following:- Identifier (Entity ID)
Enter the
Entity IDURL from the Morpheus Identity Source Integration above
- Reply URL (Assertion Consumer Service URL)
Enter the
SP ACS URLfrom the Morpheus Identity Source Integration above
- Logout URL
Enter the following format:
https://yourUrl/login/If this is a sub tenant, the format may instead be the following:https://yourUrl/login/account/1The login URL can be found under IDENTITY SOURCES in the tenant
On Step 2 (
Attributes and Claims), click theEditbuttonClick the
Add a group claimbutton at the topChoose
All groupsand ensureGroup IDis selected for theSource attributedropdownNote
You can also choose
Security groups, which ever makes more sense for the organizationClose the pane and return to the Enterprise Application in the
Single sign-onsectionOn Step 3 (
SAML Certificates), click theDownloadlink next toCertificate (Base64)andFederation Metadata XMLNote
The files will download, keep them available for later configuation in Morpheus
Navigate to
Users and Groupsin the left paneClick the
Add user/groupbuttonAdd Azure groups to this application that will be able to login to Morpheus
Note
Note the object ID for each of these groups, as they will be used later when configuring Morpheus to map the group to roles
Once groups have been added, click the
Assignbutton at the bottom
Configure the Azure AD SAML Integration in Morpheus¶
Login to Morpheus using
Username and Password, as usualNavigate to Administration > Tenants
Click a tenant hyperlink
Select IDENTITY SOURCES in the Tenant detail page
Click the pencil (edit) next to the integration created previously
Ensure the
SAML REQUESTfield is set toSelf SignedNote
A custom RSA signature can be used here if needed, if required by the orgnaization
Ensure the
SAML RESPONSEfield is set toValidate Assertion SignatureNote
With this setting, if the assertion signature ever changes in the Azure Enterprise Application, this would need to be updated to match
Edit/view the downloaded
Federation Metadata XML(.xmlextension) file from the previous sectionNote
It is recommended to use
Microsoft Edge, or another browser, to view the contentsIn the
Federation Metadata XMLfile, locate the<X509Certificate> </X509Certificate>under the<Signature>section. Copy the entire contents between the<X509Certificate>and</X509Certificate>, it is very longPaste the value copied from the
Federation Metadata XMLfile into thePublic Key (Optional)box, below theSAML RESPONSEdropdown
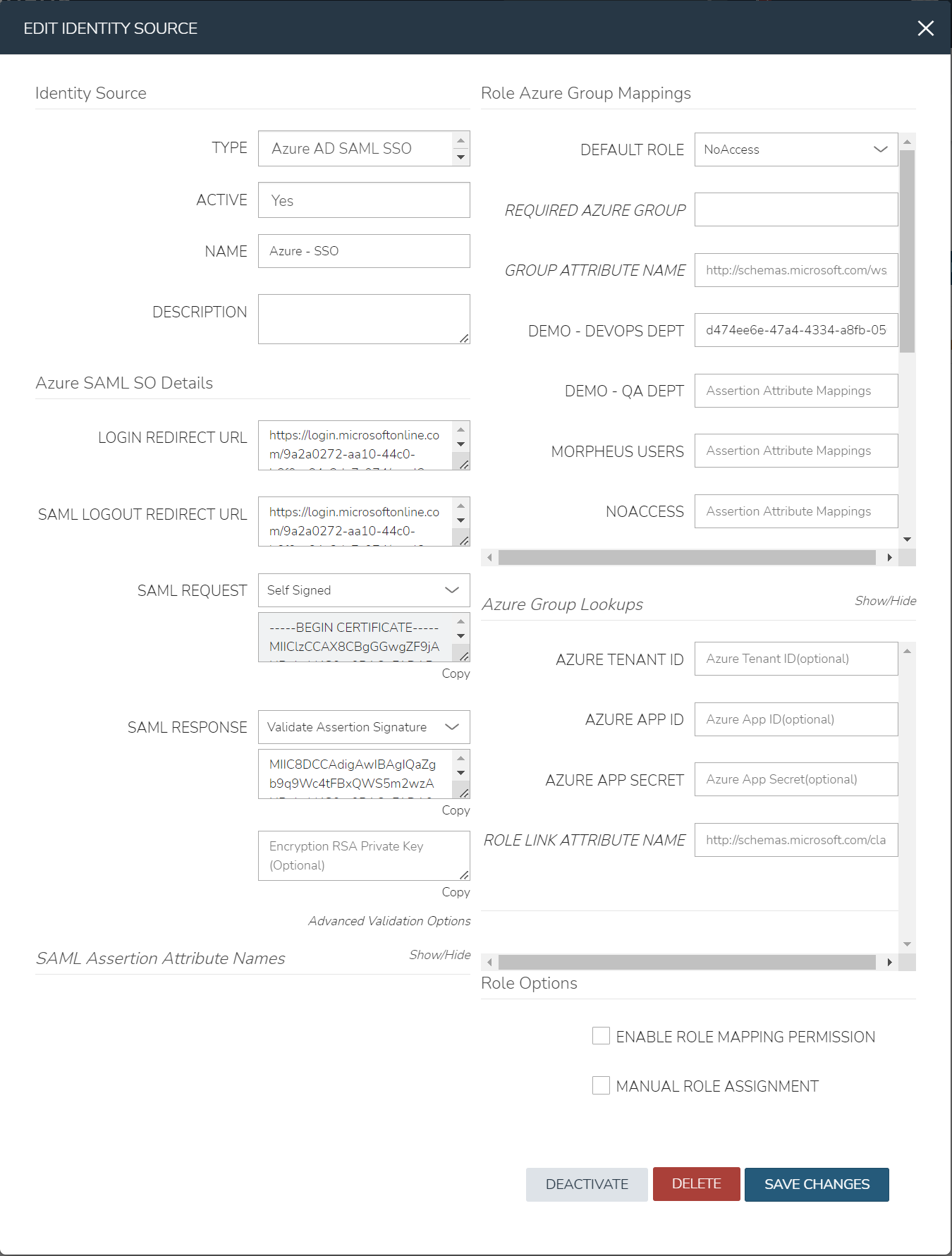
Configure Role Mappings¶
Role mappings will map Azure AD Groups to Morpheus Roles. Azure AD users will be assigned Roles in Morpheus upon signing in based on their Group Membership in Azure AD.
Important
Use an Azure Groups Object ID, not Group name, when entering Role Mappings. Example: 7626a4a2-b388-4d9b-a228-72ce9a33bd4b
- DEFAULT ROLE
Role a Azure AD user will be assigned by default upon signing in to Morpheus using this Identity Source.
- REQUIRED AZURE AD GROUP OBJECT ID
Object ID of Azure AD Group a user must be a member of to be authorized to sign in to Morpheus. Users not belonging to this Group will not be authorized to login to Morpheus. This field is optional, and if left blank, any user from the Azure AD App will be able to sign in to Morpheus and will be assigned the Default Role if no Role Mappings match AD Group membership.
- GROUP ASSERTION ATTRIBUTE NAME
Enter
http://schemas.microsoft.com/ws/2008/06/identity/claims/groupsfor Azure AD SSO- Additional Role Mappings
The existing Roles in Morpheus will be listed. To map a Morpheus Role to an Azure AD Group, enter the Object ID of the desired Azure AD Group in the Role Attribute Value field for the corresponding Morpheus Role.
Important
Use an Azure Groups Object ID, not Group name, when entering Role Mappings. Example: 7626a4a2-b388-4d9b-a228-72ce9a33bd4b
- ENABLE ROLE MAPPING PERMISSION
When selected, Tenant users with appropriate rights to view and edit Roles will have the ability to set role mapping for the Identity Source integration. This allows the Tenant user to edit only the role mappings without viewing or potentially editing the Identity Source configuration.
- MANUAL ROLE ASSIGNMENT
When selected, administrators can manually edit Roles for users created through this identity source integration from the user detail page (Administration > Users > Selected user).
Note
For more on Identity Source role mapping permissions, see the associated guide in our KnowledgeBase.
Once populated, select SAVE CHANGES and the SAML identity source integration will be added. The Identity Source can be edited anytime to deactivate or change Role Mappings or other values.
Note
If Role mappings are edited after Azure AD SSO users have signed into Morpheus, currently logged in users will need to log out of Morpheus for the new Role mappings to take effect, when applicable.
Under the
Role Azure Group Mappingssecton, verify theDEFAULT ROLEdropdown has the role in Morpheus selected that all users will be assigned by defaultIt is recommended that this role contains no permissions, which ensures that anyone who authenticates gets no access
Under the
Role Azure Group Mappingssecton, you will see role names listed. Next to these are text boxes withAssertion Attribute Mappingsinside. Enter group object IDs from Azure into these text boxes. This will map the Azure AD groups to specific roles in MorpheusFinally, click
Save Changesat the bottom of the page
Here is an example of the configuration above:
Azure Group Lookups¶
When a user in azure ad has more that 150 group attributes, Azure does not include the group claims in the SAML response, and Morpheus is required to query Microsoft Graph to obtain the users group attribute values. When there are users that are members of more that 150 groups, populate the Azure Group Lookups section in order for those users to be able to use the Azure AD SAML SSO integration, otherwise no groups will be obtained and proper role mappings cannot occur.
- AZURE TENANT ID
Add Azure AD Tenant ID if user group membership will exceed 150. See Copy Directory (tenant) and Application (client) IDs for information on obtaining an Azure AD Tenant ID
- AZURE APP ID
Add Azure AD Application (Client) ID if user group membership will exceed 150. See Copy Directory (tenant) and Application (client) IDs for information on obtaining an Azure AD Application (Client) ID
- AZURE APP SECRET
Add Azure Application (Client) Secret if user group membership will exceed 150. See Generate a Client Secret for information on creating an Azure Application (Client) Secret
- ROLE LINK ATTRIBUTE NAME
default: http://schemas.microsoft.com/claims/groups.link. This is not normally changed.
Logging Into Morpheus with Azure AD SAML¶
Navigate to the Morpheus URL
A new button will appear to allow sign-in using Azure AD SAML, with the same name as the integration. Click the button
Sign-in with your Microsoft/Azure account

Note
If no local users other than the System Admin have been created, “USERNAME AND PASSWORD” option will not be displayed, only the SAML option.
Okta¶
Overview¶
Morpheus allows users to integrate an Okta deployment for user management and authentication. In Morpheus, identity sources are added on a per-Tenant basis and Morpheus allows you to map Okta user groups to Morpheus user groups. User accounts are automatically created with matching metadata and role permissions when users are authenticated.
Adding an Okta Integration¶
Navigate to Administration > Tenants
Select a Tenant
Select IDENTITY SOURCES
Select + IDENTITY SOURCE
Choose TYPE: “Okta”
Populate the following, then select SAVE CHANGES:
- Name
Unique name for authentication type
- Description
A description for your new Okta Identity Source
- Okta URL
Your Okta URL
- Administrator API Token
Your Okta Administrator API Token
- Required Group
The Okta group that users must be in to have access (optional)
- Default Role
The default role a user is assigned if no group is listed under an Okta user that maps within the Morpheus Role Mappings section
- ENABLE ROLE MAPPING PERMISSION
When selected, Tenant users with appropriate rights to view and edit Roles will have the ability to set role mapping for the Identity Source integration. This allows the Tenant user to edit only the role mappings without viewing or potentially editing the Identity Source configuration.
- MANUAL ROLE ASSIGNMENT
When selected, administrators can manually edit Roles for users created through this identity source integration from the user detail page (Administration > Users > Selected user).
Note
For more on Identity Source role mapping permissions, see the associated guide in our KnowledgeBase.
Now, allowed Okta users can log into Morpheus via their Okta credentials and a user will be automatically generated within Morpheus with matching metadata and mapped Role permissions.
Note
If you’ve created multi-tenant roles, these will also appear here and can be mapped to Okta user groups allowing you to map users to equivalent user groups in Morpheus.
OneLogin¶
Adding OneLogin Identity Source Integration
Navigate to Administration > Tenants
Select the Tenant to add the Identity Source Integration
Select IDENTITY SOURCES
Select + IDENTITY SOURCE
Enter the following:
- TYPE
OneLogin
- NAME
Name of the Identity Source Integration in Morpheus
- DESCRIPTION
Optional Description of the Identity Source
- ONELOGIN SUBDOMAIN
- example: morpheus-dev
Warning
Please verify the subdomain carefully. An invalid subdomain will cause authentication attempts by OneLogin users to fail.
- ONELOGIN REGION
Specify US or EU region
- API CLIENT SECRET
OneLogin API Client Secret from the Settings - API section in OneLogin portal
- API CLIENT ID
OneLogin API Client ID from the Settings - API section in OneLogin portal
- REQUIRED ROLE
Enter a role of OneLogin users logging into Morpheus must have at least this OneLogin role to gain access to Morpheus.
- DEFAULT ROLE
The default Morpheus Role applied to users created from OneLogin Integration if no other role mapping is specified below
- ROLE MAPPINGS
Existing Morpheus Roles will be listed with fields to enter OneLogin Roles to map to. Users with OneLogin roles matching the role mappings will be assigned the appropriate Role(s) in Morpheus when signing in.
- ENABLE ROLE MAPPING PERMISSION
When selected, Tenant users with appropriate rights to view and edit Roles will have the ability to set role mapping for the Identity Source integration. This allows the Tenant user to edit only the role mappings without viewing or potentially editing the Identity Source configuration.
- MANUAL ROLE ASSIGNMENT
When selected, administrators can manually edit Roles for users created through this identity source integration from the user detail page (Administration > Users > Selected user).
Note
For more on Identity Source role mapping permissions, see the associated guide in our KnowledgeBase.
Select SAVE CHANGES and the OneLogin Integration will be added.
Users can now login to Morpheus with OneLogin credentials. The first Login will create a user in Morpheus matching the Username, email and Password from OneLogin. If a REQUIRED ROLE is specified in the Identity Source settings, only users with that Role in OneLogin will be able to login to Morpheus.
Important
OneLogin users will not authenticate in Morpheus if there is an existing Morpheus User with matching username or email address.
SAML Integration¶
Overview¶
The Morpheus SAML identity source integration allows customers to add user SSO to Morpheus, authenticated by external login SAML providers.

Adding a SAML Integration¶
To add a SAML integration:
Navigate to Administration > Tenants
Select a tenant.
Select IDENTITY SOURCES in the Tenant detail page
Select + ADD IDENTITY SOURCE.
Select SAML SSO from the TYPE field
Add a Name and optional Description for the SAML integration
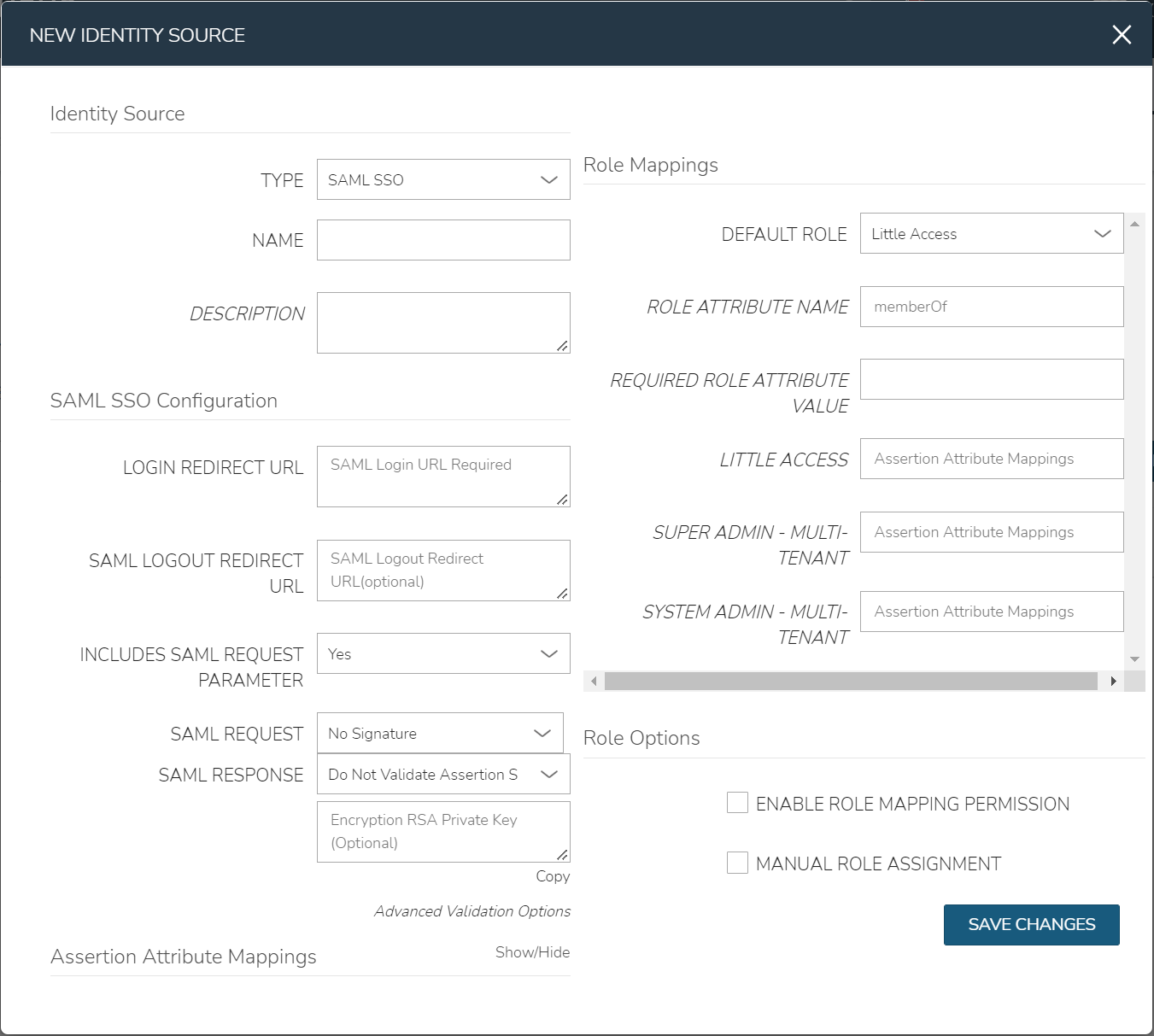
There are 4 sections with fields that need to be populated depending on the desired configuration:
SAML Configuration
Role Mappings
Role Options
Assertion Attribute Mappings
SAML Configuration¶
- LOGIN REDIRECT URL
This is the SAML endpoint Morpheus will redirect to when a user signs into Morpheus via SAML
- SAML LOGOUT REDIRECT URL
The URL Morpheus will POST to when a SAML user logs out of Morpheus
- INCLUDES SAML REQUEST PARAMETER
Yes (recommended) - the AuthN request will be sent via the ?SAMLRequest= parameter in the URL (GET)
No - the AuthN request will be submitted in the body of the request (POST)
Note
The SAML SP documentation should mention which binding to use but GET is most common
- SAML REQUEST
No Signature - No signature is used on the SAML request
Self Signed - A self-signed X.509 Certificate is gentered after clicking SAVE CHANGES. This signature value can be used by the SAML SP to verify the authenticity of the request
Custom RSA Signature - Import a custom RSA Private Key and respective X.509 Certificate. This signature value can be used by the SAML SP to verify the authenticity of the request
- SAML RESPONSE
Do Not Validate Assertion Signature - The SAML response signature from the SAML SP will not be validated
Validate Assertion Signature - The SAML reponse signature from the SAML SP will be validated. Enter the SAML SP X.509 certificate in the Public Key field. This must be in PEM format
Important
Setting SAML REQUEST to “No Signature” and SAML RESPONSE to “Do Not Validate Assertion Signature” is allowed but not recommended for security reasons.
Role Mappings¶
- DEFAULT ROLE
Role any SAML user will be assigned by default
- ROLE ATTRIBUTE NAME
The name of the attribute/assertion field that will map to Morpheus roles, such a MemberOf
- REQUIRED ROLE ATTRIBUTE VALUE
Attribute/assertion value that a user must be assigned/a member of to be authorized, such as group or role in the SAML SP. This is obtained from the attribute/assertion defined in the ROLE ATTRIBUTE NAME field
- <Morpheus ROLE NAME>
Additional roles that can be mapped to a user, which will add to the DEFAULT ROLE. Attribute value that a user must be assigned/a member of to be authorized, such as group or role in the SAML SP. This is obtained from the attribute/assertion defined in the ROLE ATTRIBUTE NAME field
Note
For more on Identity Source role mapping permissions, see the associated guide in our KnowledgeBase.
Role Options¶
- ENABLE ROLE MAPPING PERMISSION
When selected, Tenant users with appropriate rights to view and edit Roles will have the ability to set role mapping for the Identity Source integration. This allows the Tenant user to edit only the role mappings without viewing or potentially editing the Identity Source configuration.
- MANUAL ROLE ASSIGNMENT
When selected, administrators can manually edit Roles for users created through this identity source integration from the user detail page (Administration > Users > Selected user).
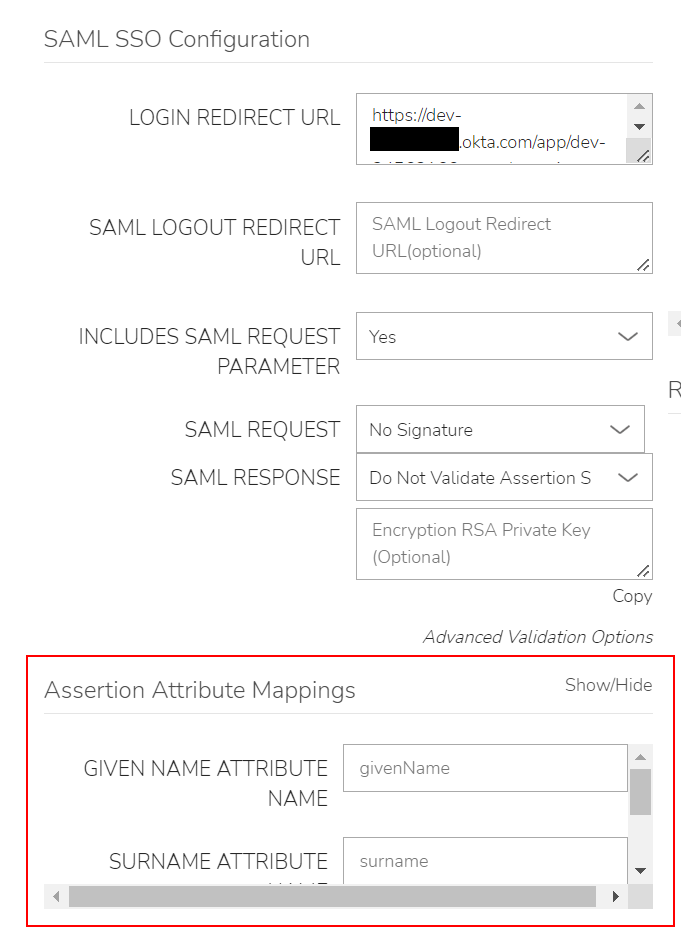
Assertion Attribute Mappings¶
- GIVEN NAME ATTRIBUTE NAME
SAML SP field value to map to Morpheus user First Name
- SURNAME ATTRIBUTE NAME
SAML SP field value to map to Morpheus user Last Name
- EMAIL ATTRIBUTE
SAML SP field value to map to Morpheus user email address
Once populated, select SAVE CHANGES and the SAML identity source integration will be added.
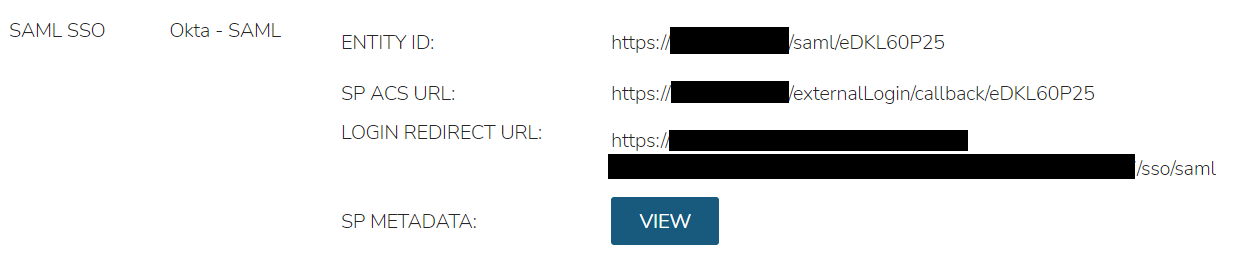
In the Identity Sources section, important information for configuration of the SAML integration is provided. Use the SP ENTITY ID and SP ACS URL for configuration on the external login SAML provider side.
Note
In some cases, the SAML provider may need these values before providing the LOGIN REDIRECT URL and other values. When creating the integration, the NAME and LOGIN REDIRECT URL can contain any values, then selecting SAVE CHANGES will generate the above values. The NAME and LOGIN REDIRECT URL can be edited later, once the SAML configuration is created in the SAML provider.
ENTITY ID
SP ACS URL
LOGIN REDIRECT URL
SP METADATA
Sample Metadata code output:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?><EntityDescriptor entityID="https://someip.com/saml/eDKL60P25" xmlns="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:metadata"><SPSSODescriptor AuthnRequestsSigned="false" WantAssertionsSigned="true" protocolSupportEnumeration="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:protocol"><NameIDFormat>urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:unspecified</NameIDFormat><AssertionConsumerService index="0" isDefault="true" Binding="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-POST" Location="https://someip.com/externalLogin/callback/eDKL60P25"/></SPSSODescriptor></EntityDescriptor>
Note
Different SAML providers will have different field names and requirements. An Okta SAML Dev environment was used for the example integration in this article.
Okta SAML SSO¶
For Okta SAML integration, the following fields are mapped:
LOGIN REDIRECT URL : Identity Provider Single Sign-On URL
ENTITY ID: Audience URI (SP Entity ID)
SP ACS URL: Single sign on URL
Onelogin SAML SSO¶
For Onelogin SAML integration, the following fields are mapped:
LOGIN REDIRECT URL : SAML 2.0 Endpoint (HTTP)
SAML LOGOUT REDIRECT URL : SLO Endpoint (HTTP)
SIGNING PUBLIC KEY : X.509 Certificate
ENTITY ID: ACS (Consumer) URL Validator
SP ACS URL: ACS (Consumer) URL