Tasks¶
Overview¶
There are many Task Types available, including scripts added directly, scripts and templates from the Library section, recipes, playbooks, puppet agent installs, and http (api) calls. Tasks are primarily created for use in Workflows, but a single Task can be executed on an existing instance via Actions > Run Task.
Role Permissions¶
The User Role Permission ‘Provisioning: Tasks FULL’ is required to create, edit and delete tasks.
Tasks Types that can execute locally against the HPE Morpheus Enterprise Appliance have an additional Role Permission: Tasks - Script Engines. Script Engine Task Types will be hidden for users without Tasks - Script Engines role permissions.
Common Options¶
When creating a Task, the required and optional inputs will vary significantly by the Task type. However, there are options which are common to Tasks of all types.
Target Options¶
When creating a Task, users can select a target to perform the execution. Some Task types allow for any of the three execution targets listed below and some will limit the user to two or just one. The table in the next section lists the available execution targets for each Task type.
Resource: A HPE Morpheus Enterprise-managed Instance or server is selected to execute the Task
Local: The Task is executed by the HPE Morpheus Enterprise appliance node
Remote: The user specifies a remote box which will execute the Task
Execute Options¶
Continue on Error: When marked, Workflows containing this Task will continue and will remain in a successful state if this Task fails
Retryable: When marked, this Task can be configured to be retried in the event of failure
Retry Count: The maximum number of times the Task will be retried when there is a failure
Retry Delay: The length of time (in seconds) HPE Morpheus Enterprise will wait to retry the Task
Allow Custom Config: When marked, a text area is provided at Task execution time to allow the user to pass extra variables or specify extra configuration. See the next section for an example.
Source Options¶
Task configuration code may be entered in a number of ways depending on the Task type. Changing the SOURCE type will often update the available fields in the Task modal to accommodate the selected sourcing. Not every Task type supports every sourcing type listed here.
Local: The Task configuration code is written directly in HPE Morpheus Enterprise in a large text area. HPE Morpheus Enterprise includes syntax highlighting for supported Task languages for easier debugging and script writing
Repository: Source the Task configuration code from an integrated Git or Github repository. This requires a pre-existing integration with a Github or other Git-based repository. See the relevant integration guides for full details on creating such an integration. Specify the path to the appropriate file through the WORKING PATH field. The appropriate branch may also be specified (if a branch other than ‘main’ is required) in the BRANCH/TAG field. To reference a tag from this field, use the following syntax:
refs/tags/<tag-name-here>. Unless otherwise specified, Task config is sourced fresh from the repository each time the Task is invoked which ensures the latest code is always usedURL: For Task configuration that can be source via an outside URL, specify the address in the URL field
Allow Custom Config¶
When “Allow Custom Config” is marked on a Task, the user is shown a text area for custom configuration when the Task is executed manually from the Tasks List Page. If the Task is to be part of an Operational Workflow, mark the same box on the Workflow rather than on the Task to see the text area at execution time. This text area is inside the “Advanced Options” section, which must be expanded in order to reveal the text area. Within the text area, add a JSON map of key-value pairs which can be resolved within your automation scripts. This could be used to pass extra variables that aren’t always needed in the script or for specifying extra configuration.
Example JSON Map:
{"key1": "value1",
"key2": "value2",
"os": "linux",
"foo": "bar"}
When the Task is executed, these extra variables would be resolved where called into the script such as in the following simple BASH script example:
echo "<%=customOptions.os%>"
echo "<%=customOptions.foo%>"
The above example would result in the following output:
linux
bar
Task Types¶
Task Type |
Task Description |
Source Options |
Execute Target Options |
Configuration Requirements |
Role Permissions Requirements |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ansible |
Runs an Ansible playbook. Ansible Integration required |
Ansible Repo (Git) |
Local, Resource |
Existing Ansible Integration |
Library: Tasks |
|
Ansible Tower |
Relays Ansible calls to Ansible Tower |
Tower Integration |
Local, Remote, Resource |
Existing Ansible Tower Integration |
Library: Tasks |
|
Chef bootstrap |
Executes Chef bootstrap and run list. Chef Integration required |
Chef Server |
Resource |
Existing Chef Integration |
Library: Tasks |
Conditional Workflow |
Allows the user to set JavaScript logic. If it resolves to |
N/A (JavaScript logic must be locally sourced, Tasks housed within the associated Workflows may have different sourcing options depending on their types.) |
Local |
Existing Operational Workflows |
Library: Tasks |
|
|
Send an email from a Workflow |
Task Content |
Local |
SMTP Configured |
Library: Tasks |
|
|
Groovy script |
Executes Groovy Script locally (on HPE Morpheus Enterprise app node) |
Local, Repository, Url |
Local |
None |
Library: Tasks, Tasks - Script Engines |
|
HTTP |
Executes REST call for targeting external API’s. |
Local |
Local |
None |
Library: Tasks |
|
Javascript |
Executes Javascript locally (on HPE Morpheus Enterprise app node) |
Local |
Local |
None |
Library: Tasks, Tasks - Script Engines |
|
jRuby Scirpt |
Executes Ruby script locally (on HPE Morpheus Enterprise app node) |
Local, Repository, Url |
Local |
None |
Library: Tasks, Tasks - Script Engines |
|
Library Script |
Creates a Task from an existing Library Script (Library > Templates > Script Templates) |
Library Script |
Resource |
Existing Library Script |
Library: Tasks |
|
Library Template |
Creates a Task from an existing Library Template (Library > Templates > Spec Templates) |
Library Template |
Resource |
Existing Library Templates |
Library: Tasks |
Nested Workflow |
Embeds a Workflow into a Task which allows the Workflow to be nested within other Workflows for situations when common Task sets are frequently used in Workflows |
N/A |
Local |
N/A |
Library: Tasks |
|
|
PowerShell Script |
Execute PowerShell Script on the Target Resource |
Local, Repository, Url |
Remote, Resource, Local |
None |
Library: Tasks |
|
Puppet Agent Install |
Executes Puppet Agent bootstrap, writes |
Puppet Master |
Resource |
Existing Puppet Integration |
Library: Tasks |
|
Python Script |
Executes Python Script locally |
Local, Repository, Url |
Local |
|
Library: Tasks, Tasks - Script Engines |
|
Restart |
Restarts target VM/Host/Container and confirms startup status before executing next task in Workflow |
System |
Resource |
None |
Library: Tasks |
|
Shell Script |
Executes Bash script on the target resource |
Local, Repository, Url |
Local, Remote, Resource |
None |
Library: Tasks |
|
vRealize Orchestrator Workflow |
Executes vRO Workflow on the Target Resource |
vRO Integration |
Local, Resource |
Existing vRO Integration |
Library: Tasks |
|
Write Attributes |
Add arbitrary values to the Attributes map of the target resource |
N/A |
Local |
Provide map of values as valid JSON |
Library: Tasks |
Task Configuration¶
Ansible Playbook

NAME: Name of the Task
CODE: Unique code name for API, CLI, and variable references
ANSIBLE REPO: Select existing Ansible Integration
GIT REF: Specify tag or branch (Option, blank assumes default)
PLAYBOOK: Name of playbook to execute, both
playbookandplaybook.ymlformat supportedTAGS: Enter comma separated tags to filter executed tasks by (ie
--tags)SKIP TAGS: Enter comma separated tags to run the playbook without matching tagged tasks (ie
--skip-tags)
Important
Using different Git Refs for multiple Ansible Tasks in same Workflow is not supported. Git Refs can vary between Workflows, but Tasks in each Workflow must use the same Git Ref.
Ansible Tower Job

NAME: Name of the Task
CODE: Unique code name for API, CLI, and variable references
TOWER INTEGRATION: Select an existing Ansible Tower integration
INVENTORY: Select an existing Inventory, when bootstrapping an Instance, HPE Morpheus Enterprise will add the Instance to the Inventory
GROUP: Enter a group name, when bootstrapping an Instance, HPE Morpheus Enterprise will add the Instance to the Group if it exists. If it does not exist, HPE Morpheus Enterprise will create the Group
JOB TEMPLATE: Select an existing job template to associate with the Task
SCM OVERRIDE: If needed, specify an SCM branch other than that specified on the template
EXECUTE MODE: Select Limit to Instance (template is executed only on Instance provisioned), Limit to Group (template is executed on all hosts in the Group), Run for all (template is executed on all hosts in the Inventory), or Skip Execution (to skip execution of the template on the Instance provisioned)
Chef bootstrap

NAME: Name of the Task
CODE: Unique code name for API, CLI, and variable references
CHEF SERVER: Select existing Chef integration
ENVIRONMENT: Populate Chef environment, or leave as
_defaultRUN LIST: Enter Run List, eg
role[web]DATA BAG KEY: Enter data bag key (will be masked upon save)
DATA BAG KEY PATH: Enter data bag key path, eg
/etc/chef/databag_secretNODE NAME: Defaults to Instance name, configurable
NODE ATTRIBUTES: Specify attributes inside the
{}
Conditional Workflow
NAME: Name of the Task
CODE: Unique code name for API, CLI, and variable references
LABELS: A comma separated list of Labels for organizational purposes. See elsewhere in HPE Morpheus Enterprise docs for additional details on utilizing Labels
CONDITIONAL (JS): JavaScript logic which determines the Operational Workflow which is ultimately run. If it resolves to
true, the “If” Workflow is run and if it resolves tofalsethe “Else” Workflow is runIF OPERATIONAL WORKFLOW: Set the Operational Workflow which should be run if the JavaScript conditional resolves to
trueELSE OPERATIONAL WORKFLOW: Set the Operational Workflow which should be run if the JavaScript conditional resolves to
false
Groovy script

NAME: Name of the Task
CODE: Unique code name for API, CLI, and variable references
RESULT TYPE: Single Value, Key/Value Pairs, or JSON
CONTENT: Contents of the Groovy script if not sourcing it from a repository
Email

NAME: Name of the Task
CODE: Unique code name for API, CLI, and variable references
SOURCE: Choose local to draft or paste the email directly into the Task. Choose Repository or URL to bring in a template from a Git repository or another outside source
EMAIL ADDRESS: Email addresses can be entered literally or HPE Morpheus Enterprise automation variables can be injected, such as
<%=instance.createdByEmail%>SUBJECT: The subject line of the email, HPE Morpheus Enterprise automation variables can be injected into the subject field
CONTENT: The body of the email is HTML. HPE Morpheus Enterprise automation variables can be injected into the email body when needed
SKIP WRAPPED EMAIL TEMPLATE: The HPE Morpheus Enterprise-styled email template is ignored and only HTML in the Content field is used
Tip
To whitelabel email sent from Tasks, select SKIP WRAPPED EMAIL TEMPLATE and use an HTML template with your own CSS styling
HTTP (API)

NAME: Name of the Task
CODE: Unique code name for API, CLI, and variable references
RESULT TYPE: Single Value, Key/Value Pairs, or JSON
URL: An HTTP or HTTPS URL as the HTTP Task target
HTTP METHOD: GET (default), POST, PUT, PATCH, HEAD, or DELETE
AUTH USER: Username for username/password authentication
PASSWORD: Password for username/password authentication
BODY: Request Body
HTTP HEADERS: Enter requests headers, examples below:
Authorization
Bearer token
Content-Type
application/json
IGNORE SSL ERRORS: Mark when making REST calls to systems without a trusted SSL certificate
Javascript

NAME: Name of the Task
CODE: Unique code name for API, CLI, and variable references
RESULT TYPE: Single Value, Key/Value Pairs, or JSON
SCRIPT: Javascript contents to execute
jRuby Script

NAME: Name of the Task
CODE: Unique code name for API, CLI, and variable references
RESULT TYPE: Single Value, Key/Value Pairs, or JSON
CONTENT: Contents of the jRuby script is entered here if it’s not being called in from an outside source
Library Script

NAME: Name of the Task
CODE: Unique code name for API, CLI, and variable references
RESULT TYPE: Single Value, Key/Value Pairs, or JSON
SCRIPT: Search for an existing script in the typeahead field
Library Template

NAME: Name of the Task
CODE: Unique code name for API, CLI, and variable references
TEMPLATE: Search for an existing template in the typeahead field
Nested Workflow
Powershell Script
NAME: Name of the Task
CODE: Unique code name for API, CLI, and variable references
RESULT TYPE: Single Value, Key/Value Pairs, or JSON
VERSION: Select the version of Powershell this Task should run in. Powershell 5 is the default selection, Powershell 6 or 7 must be installed on the target to select those versions
ELEVATED SHELL: Run script with administrator privileges
IP ADDRESS: IP address of the PowerShell Task target
PORT: SSH port for PowerShell Task target (5985 default)
USERNAME: Username for PowerShell Task target
PASSWORD: Password for PowerShell Task target
Content: Enter script to execute if not calling the script in from an outside source
Note
Setting the execution target to local requires Powershell to be installed on the HPE Morpheus Enterprise appliance box(es). Microsoft Documentation contains installation instructions for all major Linux distributions and versions.
Puppet Agent Install

NAME: Name of the Task
CODE: Unique code name for API, CLI, and variable references
PUPPET MASTER: Select Puppet Master from an existing Puppet integration
PUPPET NODE NAME: Enter Puppet node name. Variables supported eg.
<%= instance.name %>PUPPET ENVIRONMENT: Enter Puppet environment, eg.
production
Python Script

Important
Python Tasks use virtual environments. For this reason,
virtualenvmust be installed on your appliances in order to work with Python Tasks. See the information below for more detailed steps to installvirtualenvon your HPE Morpheus Enterprise appliance node(s).NAME: Name of the Task
CODE: Unique code name for API, CLI, and variable references
RESULT TYPE: Single Value, Key/Value Pairs, or JSON
CONTENT: Python script to execute is entered here if not pulled in from an outside repository
COMMAND ARGUMENTS: Optional arguments passed into the Python script. Variables supported eg.
<%= instance.name %>ADDITIONAL PACKAGES: Additional packages to be installed after
requirements.txt(if detected). Expected format for additional packages: ‘packageName==x.x.x packageName2==x.x.x’, the version must be specifiedPYTHON BINARY: Optional binary to override the default Python binary
Note
When troubleshooting errors in Python scripts using line numbers reported in HPE Morpheus Enterprise UI (such as in Task execution histories), you must subtract four line numbers to arrive at the correct line in the Python document. This is because HPE Morpheus Enterprise injects four lines at execution time to add HPE Morpheus Enterprise environment variables.
Enterprise Proxy Considerations
Additional considerations must be made in enterprise proxy environments where Python Tasks are run with additional package download requirements. These additional packages are downloaded using
pipand may not obey global HPE Morpheus Enterprise proxy rules. To deal with this, create or edit the pip configuration file at/etc/pip.conf. Your configuration should include something like the following:[global] proxy = http://some-proxy-ip.com:8087
For more information, review the Pip documentation on using proxy servers here.
CentOS 7 / Python 2.7 (RHEL system Python)
With a fresh install of HPE Morpheus Enterprise on a default build of CentOS 7, Python Tasks will not function due to the missing requirement of
virtualenv.If you attempt to run a python task, you will get an error similar to the following:
Task Execution Failed on Attempt 1 sudo: /tmp/py-8ae51ebf-749c-4354-b6e4-11ce541afad5/bin/python: command not found
In order to run HPE Morpheus Enterprise Python Tasks in CentOS 7, install
virtualenv:yum install python-virtualenvIf you require
python3, you can specify the binary to be used while building the virtual environment. In a default install, do the following:yum install python3. Then, in your HPE Morpheus Enterprise Python Task, specify the binary in the PYTHON BINARY field as “/bin/python3”. This will build a virtual environment in/tmpusing thepython3binary, which is equivalent to making a virtual environment like so:virtualenv ~/venv -p /bin/python3.If you wish to install additional Python packages into the virtual environment, put them in
pipformat and space-separated into the ADDITIONAL PACKAGES field on the Python Task. Use the help text below the field to ensure correct formatting.CentOS 8 and Python
In CentOS 8, Python is not installed by default. There is a
platform-pythonbut that should not be used for anything in userland. The error message with a default install of CentOS 8 will be similar to this:Task Execution Failed on Attempt 1 sudo: /tmp/py-cffc9a8f-c40d-451d-956e-d6e9185ade33/bin/python: command not found
The default
virtualenvfor CentOS 8 is the python3 variety, for HPE Morpheus Enterprise to use Python Tasks, do the following:yum install python3-virtualenvIf Python2 is required, do the following:
yum install python2and specify/bin/python2as the PYTHON BINARY in your HPE Morpheus Enterprise Task.This will build a
virtualenvin/tmpusing thepython2binary, which is equivalent to making avirtualenvlike so:virtualenv ~/venv -p /bin/python2If you wish to install additional Python packages into the virtual environment, put them in
pipformat and space-separated into the ADDITIONAL PACKAGES field on the Python Task. Use the help text below the field to ensure correct formatting.Restart

NAME: Name of the Task
CODE: Unique code name for API, CLI, and variable references
Shell Script

NAME: Name of the Task
CODE: Unique code name for API, CLI, and variable references
RESULT TYPE: Single Value, Key/Value Pairs, or JSON
SUDO: Mark the box to run the script as
sudoCONTENT: Script to execute is entered here if not pulled in from an outside repository
Tip
When the EXECUTE TARGET option is set to “Local” (in other words, the Task is run on the appliance itself), two additional fields are revealed: GIT REPO and GIT REF. Use GIT REPO to set the PWD shell variable (identifies the current working directory) to the locally cached repository (ex. /var/opt/morpheus-node/morpheus-local/repo/git/76fecffdf1fe96516e90becdab9de) and GIT REF to identify the Git branch the Task should be run from if the default (typically main or master) shouldn’t be used. If these options are not set, the working folder will be /opt/morpheus/lib/tomcat/temp which would not allow scripts to reference file paths relative to the repository (if needed).
vRealize Orchestrator Workflow

NAME: Name of the Task
CODE: Unique code name for API, CLI, and variable references
RESULT TYPE: Single Value, Key/Value Pairs, or JSON
vRO INTEGRATION: Select an existing vRO integration
WORKFLOW: Select a vRO workflow from the list synced from the selected integration
PARAMETER BODY (JSON):
Write Attributes

NAME: Name of the Task
CODE: Unique code name for API, CLI, and variable references
ATTRIBUTES: A JSON map of arbitrary values to write to the attributes property of the target resource
Tip
This is often useful for storing values from one phase of a Provisioning Workflow for access in another phase. See the video demo below for a complete example.
There are a number of ways that a JSON payload can be statically drafted within a Write Attributes Task or called into the Task as a result from a prior Task. Consider the following examples:
To pass in a static JSON map with static values, use the format shown below.
{ "my_key1": "my_value1", "my_key2": "my_value2" }
To pass in a static JSON map with dynamic values seeded from prior Task results, ensure the RESULT TYPE value of one or more of the prior Tasks in the Workflow phase is set to “Single Value” and refer to the values within the JSON map as shown in the next example. Note that “taskCode1” and “taskCode2” refer to the CODE field value for the Task whose output you wish to reference.
{ "my_key1": "<%=results.taskCode1%>", "my_key2": "<%=results.taskCode2%>" }
To pass in a dynamic JSON map returned from a prior Task, format your Write Attributes Task as shown in the next example. Ensure that the RESULT TYPE value for the Task returning a JSON map is set to “JSON”. Note that “taskCode” in the example refers to the CODE field value for the Task being referenced. In order for the JSON map to be set correctly and able to be referenced from future Tasks, you must set the “instances” key and call the
encodeAsJSON()Groovy method as shown in the example.{ "instances": <%=results.taskCode?.encodeAsJSON()%> }
Task Management¶
Adding Tasks¶
Select Automation from within the Library menu
On the Tasks tab, click the Add button
From the New Task Wizard input a name for the task
Select the type of task from from the type dropdown
Input the appropriate configuration details. These will vary signficiantly based on the selected Task type. More details on each Task type are contained in the preceding sections.
Once done, click SAVE CHANGES
Tip
When writing a Task config, it’s often necessary to reference HPE Morpheus Enterprise variables which pertain to the specific Instance the Task is being run against. HPE Morpheus Enterprise includes a pop-out column along the right side of the Add/Edit Task modal which lists available variables. Click and drag the relevant variable into the config area and HPE Morpheus Enterprise will automatically fill in the variable call formatted for the currently chosen Task type. See the screenshot below.
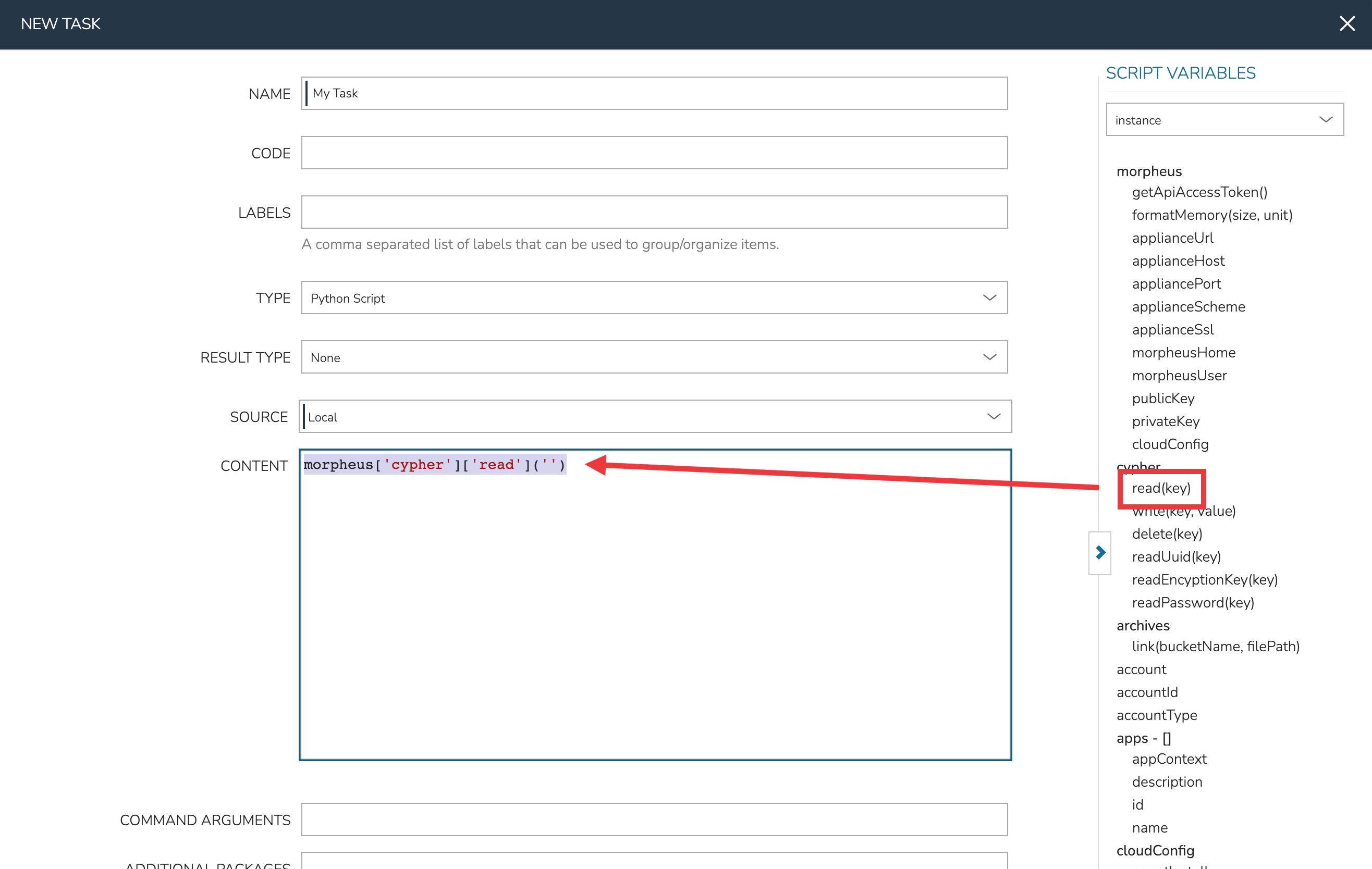
Editing Tasks¶
Select Automation from within the Library menu
Click the pencil icon (✎) on the row of the task you wish to edit
Modify Task as needed
Once done, click SAVE CHANGES
Deleting Tasks¶
Select Automation from within the Library menu
Click the trash icon (🗑) on the row of the Task you wish to delete
Task Results¶
Overview¶
Using Task results, the output from any preceding Tasks within the same Workflow phase is available to be called into additional Tasks. The results are stored on the results variable. Since results are available to all Tasks, we can use results from any or all prior Tasks so long as they are executed within the same provision phase.
In script type tasks, if a RESULT TYPE is set, HPE Morpheus Enterprise will store the output on the results variable. It’s important to understand that the result type indicates the format of the Task output HPE Morpheus Enterprise should expect. HPE Morpheus Enterprise will parse that output into a Groovy map which can be retrieved and further parsed by resolving the results variable. If the RESULT TYPE is incorrectly set, HPE Morpheus Enterprise may not be able to store the Task results correctly. Jump to the section on Script Config Examples to see how script results are processed in various example cases.
Results Types¶
- Single Value
Entire task output is stored in
<%=results.taskCode%>or<%=results["Task Name"]%>variable.
- Key/Value pairs
Expects
key=value,key=valueoutput. Entire task output is available with<%=results.taskCode%>or<%=results["Task Name"]%>variable (output inside[]). Individual Values are available with<%=results.taskCode.key%>variables.
- JSON
Expects
key:value,key:valuejson formatted output. Entire task output is available with<%=results.taskCode%>or<%=results["Task Name"]%>variable (output inside[]). Individual Values are available with<%=results.taskCode.key%>variables.
Important
The entire output of a script is treated as results, not just the last line. Ensure formatting is correct for the appropriate result type. For example, if Results Type is json and the output is not fully json compatible, the result would not return properly.
Important
Task results are not supported for Library Script task types
Script Config Examples¶
- Single Value using Task Code
- Source Task Config
NAME: Var Code (single)
CODE: singleExample
RESULT TYPE: Single Value
SCRIPT:
echo "string value"
Source Task Output:
string value- Results Task Config (using task code in variable)
NAME: N/A
CODE: N/A
RESULT TYPE: N/A
SCRIPT:
echo "single: <%=results.singleExample%>"
Results Task Output:
single: string value- Single Value using Task Name
- Source Task Config
- NAME
Var Code
- CODE
none
- RESULT TYPE
Single Value
- SCRIPT
echo "string value"
- Source Task Output
string value- Results Task using task name in variable
- Results Task Script
echo "task name: <%=results["Var Code"]%>"- Results Task Output
task name: test value
- Key/Value Pairs
- Source Task Config
- NAME
Var Code (keyval)
- CODE
keyvalExample
- RESULT TYPE
Key/Value pairs
- SCRIPT
echo "flash=bang,ping=pong"
- Source Task Output
flash=bang,ping=pong- Results Task for all results
- Results Task Script
echo "keyval: <%=results.keyvalExample%>"- Results Task Output
keyval: [flash:bang, ping:pong]
- Results Task for a single value)
- Results Task Script
echo "keyval value: <%=results.keyvalExample.flash%>"- Results Task Output
keyval value: bang
- JSON
- Source Task Config
- NAME
Var Code (json)
- CODE
jsonExample
- RESULT TYPE
JSON
- SCRIPT
echo "{\"ping\":\"pong\",\"flash\":\"bang\"}"
- Source Task Output
{"ping":"pong","flash":"bang"}- Results Task for all results
- Results Task Script
echo "json: <%=results.jsonExample%>"- Results Task Output
json: [ping:pong, flash:bang]
- Results Task for a single value
- Results Task Script
echo "json value: <%=results.jsonExample.ping%>"- Results Task Output
json value: pong
- Multiple Task Results
- Results Task Script
echo "single: <%=results.singleExample%>" echo "task name: <%=results["Var Code"]%>" echo "keyval: <%=results.keyvalExample%>" echo "keyval value: <%=results.keyval.flash%>" echo "json: <%=results.jsonExample%>" echo "json value: <%=results.jsonExample.ping%>"
- Results Task Output
single: string value task name: string value keyval: [flash:bang, ping:pong] keyval value: bang json: [ping:pong, flash:bang] json value: pong
Workflow Config¶
Add one or multiple tasks with Results Type configured to a workflow, and the results will be available to all tasks in the same phase of the workflow via the <%=results.variables%> during the workflow execution.
Task Results are only available to tasks in the same workflow phase
Task Results are only available during workflow execution